Are You Getting Enough Magnesium?
Magnesium is an essential mineral your body needs every day to function properly. From keeping your heart healthy to supporting strong bones, this nutrient plays a role in hundreds of biochemical processes. Yet, despite its importance, many people don’t get enough magnesium from their diet.
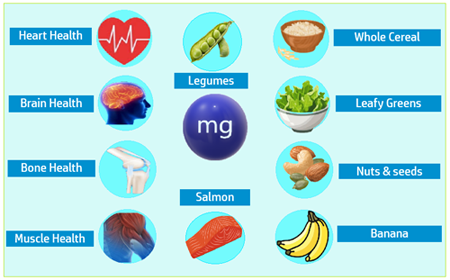
Why Magnesium Is Important for Your Body
✅ Magnesium is one of the chief macro-minerals that nearly every system in the human body requires. Here are some of its most crucial roles:
✅ Bone health – Magnesium contributes to the structural development of bones.
✅ Genetic material – It’s necessary for the synthesis of DNA, RNA, and the antioxidant glutathione.
✅ Enzyme function – Acts as a cofactor in more than 300 enzyme systems, supporting processes like protein synthesis, blood sugar control, and blood pressure regulation.
✅ Nervous and muscular system – Helps maintain proper muscle contraction and nerve signaling.
✅ Mineral balance – Plays a role in the transport of calcium and potassium, essential for heart rhythm and cellular health.
Who Is at Risk of Magnesium Deficiency?
Some groups are more vulnerable to magnesium inadequacy than others:
1 People with Gastrointestinal Diseases
-
Conditions like Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, or chronic diarrhea reduce absorption and lead to magnesium loss.
2 People with Type 2 Diabetes
3 Individuals with Alcohol Dependence
-
Alcoholism contributes to poor dietary intake, gastrointestinal problems, and kidney dysfunction—all of which increase the risk of magnesium depletion.
4 Older Adults
-
Age-related changes, such as reduced gut absorption and increased urinary excretion, make magnesium deficiency more common among seniors.
Magnesium and Its Role in Health
Low magnesium intake over time can disrupt essential biochemical pathways, increasing the risk of chronic conditions. Here are four major health areas where magnesium plays a protective role:
1 Hypertension and Cardiovascular Health
Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure and supports heart rhythm. Low levels may be linked to hypertension and increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
2 Type 2 Diabetes
Magnesium plays a role in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Adequate intake may help reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
3 Osteoporosis
Since magnesium supports bone structure and calcium balance, low intake can contribute to weaker bones and higher risk of osteoporosis.
4 Migraine Headaches
Research suggests magnesium may reduce the frequency and severity of migraines in some individuals.
Magnesium Deficiency: What You Need to Know
While severe deficiency is rare, many people may not meet their daily magnesium needs, especially due to poor dietary patterns.
Early Signs of Magnesium Deficiency:
-
Loss of appetite
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Muscle cramps or spasms
If left untreated, deficiency may worsen and contribute to chronic health problems.
Recommended Daily Intake of Magnesium
The amount of magnesium you need depends on your age and gender.
Needs increase during pregnancy and lactation.
Best Food Sources of Magnesium :
✅ Green leafy vegetables – Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard
✅ Legumes – Lentils, chickpeas, black beans
✅ Nuts and seeds – Almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, chia seeds
✅ Whole grains – Brown rice, quinoa, oats
✅ Other sources – Avocados, bananas, fatty fish, and fortified foods
On average, the body absorbs about 30% to 40% of the magnesium we consume from food. Factors like age, gut health, and certain medical conditions can influence absorption.
Quick Tips to Increase Magnesium Naturally
-
Sprinkle pumpkin seeds or chia seeds on salads, yogurt, or smoothies.
-
Swap white rice and bread for whole grain versions.
-
Add more leafy greens like spinach and kale to meals.
-
Enjoy a small piece of dark chocolate as a magnesium-rich treat.
Medical Disclaimer :
Be mindful if you fall into a higher-risk group for deficiency. Consult your healthcare provider if you suspect low magnesium or consider supplementation.
Taking small dietary steps today can help protect your long-term health.
Read further on:
≺≺ Why is regular table salt considered unhealthy?
≺≺ What makes Himalayan salt different from regular table salt?
≺≺ How are artificial sweeteners made?
≺≺ How toxic are the nitrites used in curing processed meats?
≺≺ What health problems are linked to consuming corn syrup?
≺≺ What food is most effective for moderating blood sugar?
≺≺ How Do Sugary Meals and Beverages Harm Dental Health?
≺≺ What Is the Ketogenic Diet? Is the Keto Diet Right for Everyone?
≺≺ What is the Okinawan diet? What is the secret behind Okinawan long life expectancy?
≺≺ EWG’s- The Clean Fifteen: Fruits and Vegetables with the Lowest Pesticide Levels.
≺≺ What are antioxidants? How antioxidants in the fruits and vegetables help in preventing cancers and diseases?
≺≺ What foods should people with high blood pressure avoid?
≺≺ How can I reduce the risk of cancer-causing chemicals when cooking or grilling meat?
≺≺ What happens to my blood vessels when I gain weight?
≺≺ What type of exercise is best for lowering my blood sugar?
≻≻ Watch this page for more such informative articles on Health, Nutrition, and Wellness.
≻≻-Back to Home page.
Further reading (External Links opens in new window):
≺≺- National Institute of Health – Magnesium.

